Google's BERT Algorithm in 2025: How ModernBERT Influences SEO
In the past, search engines and neural networks understood text quite primitively — they searched for individual words without considering the context. This led to inaccurate results, as algorithms confused word meanings and provided irrelevant responses. In 2018, Google introduced BERT, marking a breakthrough in natural language processing (NLP).
What is BERT?
BERT is an open machine learning framework for natural language processing. Its goal is to help computers understand the meaning of ambiguous expressions by using context.
The BERT algorithm (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) is based on transformers — a deep learning model where each output element is connected to every input element. These connections are dynamically calculated based on interrelations.
Previous language models processed text in only one direction — either left to right or right to left. BERT, however, can analyze text in both directions simultaneously. BERT has influenced the further development of AI. Its training methods have been used in models like GPT-2, ChatGPT, and other modern language models.
Stages of BERT Algorithm Development
- 2018: Google introduced BERT and made it open-source. During the research phase, the model showed outstanding results in sentiment analysis, text classification, and disambiguation.
- October 2019: Google announced the integration of the technology into its search algorithms in the United States. The understanding of search queries improved by approximately 10%.
- December 2019: BERT was extended to more than 70 languages. This impacted voice search and increased the accuracy of search engine results.
BERT in 2025: ModernBERT
At the end of 2024, Google introduced an enhanced version of the algorithm — ModernBERT. It supports longer texts of up to 8192 tokens. This means that the tool has become better at understanding the context in articles, documents, and books, not just in short phrases.
ModernBERT features a new system for understanding word order called Rotary Positional Encoding (RoPE). Traditional neural networks add special markers to indicate which word comes earlier and which comes later. The word order understanding system more flexibly determines the positions between tokens.
Another innovation is the removal of padding. Previously, when the model analyzed several texts simultaneously, shorter ones were supplemented with empty fillers. This was done to ensure all texts were of the same length; otherwise, parallel computation was impossible. ModernBERT has learned to bypass this limitation and now does not spend time and resources processing unnecessary symbols.
Previously, the model would either look at the entire text at once or only at the nearest words. Now, it first analyzes the nearest context (local attention) and then considers the entire text (global attention). This helps better understand the meaning of sentences and speeds up the process.
The model was trained on an enormous array of texts — not only articles and books but also programming code, scientific papers, and web documents. Search has become more accurate and deeper.
Influence of the BERT Algorithm on Search Results
The model has revolutionized the approach to search engine optimization. Previously, Google relied on exact matches of keywords. However, BERT has enabled the search engine to better interpret the meaning of queries.
SEO specialists now need to shift their focus from keywords to the topic and the user's intent. This is closely related to the website’s usability and the logical structure of its content. The more useful the content is to the user, the higher the website will rank in search results.
BERT has enhanced the understanding of long conversational queries, which more accurately reflect the user's needs. As a result, long-tail keywords have become more significant for SEO.
Content quality has become more important than keyword density. Previously, websites could gain prominence by overloading their text with popular queries. BERT has shifted priorities — now, the system favors deep and useful content that fully addresses the user's query.
BERT has improved Google's ability to generate featured snippets, which are used in regular searches and voice assistants. This means that specialists need to optimize pages for voice queries, which typically start with questions such as "how," "why," or "what is."
The BERT model better understands synonyms and related concepts, allowing the search engine to deliver more relevant results. Consequently, SEO strategies must now include semantic variations of keywords and consider related topics.
How to Optimize a Website for the BERT Algorithm: 5 Practical Tips
1. BERT analyzes the context of a query, so it is crucial that the page provides a comprehensive answer to the user's question.
How to use it? Study the audience's questions and needs, and write detailed and useful articles. Include natural phrases similar to how people formulate queries. Avoid keyword stuffing.
Example: Instead of "Buy the best running sneakers cheaply," write "How to choose comfortable running sneakers and what to pay attention to."
2. BERT understands natural, conversational language well. The simpler and clearer the text, the higher the likelihood that Google will interpret it correctly.
How to use it? Avoid complex phrasing—use simple words and short sentences. Avoid complex terminology and bureaucratic language. Use synonyms and natural variations of key phrases.
Example: Instead of "When selecting shoes for sports activities and training, it is important to consider the supination and pronation of the foot," write "When choosing sneakers, it is important to consider whether the foot rolls outward or inward."
3. BERT better perceives logically organized content, so a well-thought-out structure is necessary.
How to use it? Add headings (H2, H3, H4) to divide the text, and insert lists and tables to make the information easier to perceive.
4. BERT has made voice search more accurate. However, orally, people formulate queries differently than in text — this needs to be considered.
How to use it? Add interrogative headings—"how," "why," "what." Write in a "question-answer" format. Provide clear and concise answers to appear in the featured snippet.
Example: "White sneakers can be cleaned using soapy water and a soft brush. Do not use bleach to avoid damaging the material."
5. BERT continues to learn, and outdated articles may lose their rankings.
How to use it? Update articles with data, examples, and statistics. Add current information if user queries have changed. Periodically revise wording to make the text more understandable.
Principles of BERT Algorithm Operations
Most natural language processing models are trained on annotated datasets that are manually compiled by linguists. In contrast, the BERT algorithm was pre-trained on unannotated texts — specifically, the English-language Wikipedia and the Brown Corpus of English-language samples.
Through unsupervised learning, BERT continues to improve its processing of search queries in Google. The tool uses transfer learning — after pre-training on vast amounts of data, the model can be further trained for specific tasks.
Technologies underpinning BERT's operation include:
Transformers. This allows the model to consider the entire context of a sentence rather than analyzing words individually. Earlier algorithms would assign a fixed vector to each word.
Masked Language Modeling (MLM). Traditional models with vector representations have fixed meanings for words, making them less effective in context analysis. BERT uses word masking, where 15% of the words in each sequence are replaced with a token. The model then attempts to predict the original value of the masked words based on the context provided by the other, unmasked words in the sequence.
Self-attention Mechanism. The tool analyzes the relationships between words considering their surroundings. This is crucial in complex sentences. For instance, in the query "The woman stopped by the alley because there were flowers on it," BERT correctly identifies that "on it" refers to "alley" rather than "woman."
Next Sentence Prediction (NSP). BERT learns to distinguish between logically connected and random pairs of sentences.
Where Google BERT Algorithm is Used
The primary application of BERT is the effective interpretation of queries in the Google search engine. However, the company also uses this model in other projects:
- PatentBERT — for patent classification;
- DocBERT — for document classification;
- BioBERT — for analyzing medical and biological texts;
- VideoBERT — for processing video and text on YouTube;
- SciBERT — for the analysis of scientific articles;
- G-BERT — for medical recommendations.
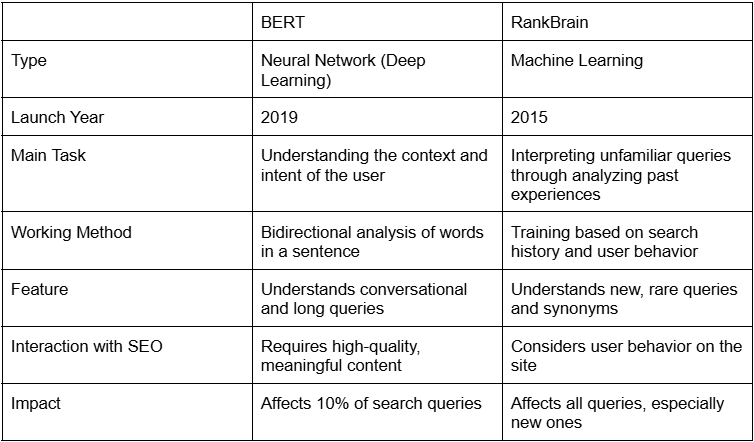
Comparison of BERT and RankBrain Algorithms: Key Differences
In addition to BERT, Google uses the RankBrain algorithm to enhance the understanding of user queries and deliver more relevant results. Although both tools are related to natural language processing, they perform different tasks and complement each other.
Google uses both technologies depending on the type of query:
- BERT assists with conversational queries, long phrases, and complex formulations.
- RankBrain analyzes new queries, synonyms, and context based on previous data.
Summary
The BERT algorithm marks a significant advancement in enabling search engines to understand natural human language rather than merely matching words. It has already enhanced the quality of Google searches, made chatbots smarter, and helped automate text analysis.
Marketers and SEO specialists need to adapt their content to meet new requirements, as the BERT algorithm continues to evolve in 2025.
Connect your website to our platform to monitor rankings and identify issues with maximum convenience. You will receive notifications about any changes on your site within 24 hours — before the problem becomes significant.
FAQ
What is BERT and why is it important?
BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) is an algorithm that helps search engines better understand the meaning of text. It analyzes words in the context of the entire sentence rather than individually. For example, if asked, "Can you get vaccinated if you are sick?", BERT understands that the question pertains to vaccination during illness rather than the individual words "vaccinated" and "sick."
How is BERT different from previous algorithms?
Previously, search engines analyzed text either from left to right or right to left. BERT reads the entire sentence and considers context. For instance, in the query "data bank," it understands that it refers to a storage of information, not a financial institution.
How does BERT affect SEO and content?
The technology evaluates the quality and usefulness of texts, so merely adding keywords is no longer effective. It is important to write clear and helpful texts that answer users' questions and avoid robotic phrasing.
Can BERT be bypassed with SEO?
Not in the traditional sense. BERT analyzes the meaning of the text rather than keywords. The best way to improve site visibility is to create logically structured, useful content written in natural language.
How does BERT affect voice search?
BERT improves the understanding of conversational queries. For example, previously, the search engine responded only to short phrases like "weather New York tomorrow," but now it correctly processes natural questions: "What will the weather be like in New York tomorrow?"
🍪 By using this website, you agree to the processing of cookies and collection of technical data to improve website performance in accordance with our privacy policy.