How to improve your website’s indexing on Google
Some relevant ways to get Google to index your site faster.
Contents:
- How to check your pages’ indexing
- Common problems with indexing on Google
- How to boost indexing speed on Google
- FAQ: what affects the indexing speed.
The faster your site appears on Google’s SERP, the sooner it becomes available for the users, the sooner it starts getting traffic and conversion. Also, it would more likely be regarded as the original source of the contents it presents. Unfortunately, you cannot be one hundred percent sure, because Google often regards the more influential site as the original source.
There’s no way to tell when exactly the Google bot will scan your webpage, and when it will appear on the SERP. That depends on the size and optimization of the website.
How to check your page indexing in a few clicks
Check the indexing pattern
A basic way to do so is entering Google Search Console and looking at the “Coverage” chart on the “Overview” page.

The green line indicates pages without errors and the red line - the ones containing them. Open the “coverage” report to see what indexing error occurred and when exactly Googlebot discovered it.
You can use our website audit service to check your web-pages indexing rate and see if any filters were applied to your sites by Google.
It will also give you information about traffic, backlinks, relevance to search queries, loading speed and other parameters. It is in some way similar to PageSpeed Insights, but also provides useful advice.
Check the status of a specific page
To do so simply type the page’s URL into the search bar of the Google Search Console. If your page is not in the index, you will receive a corresponding notification.
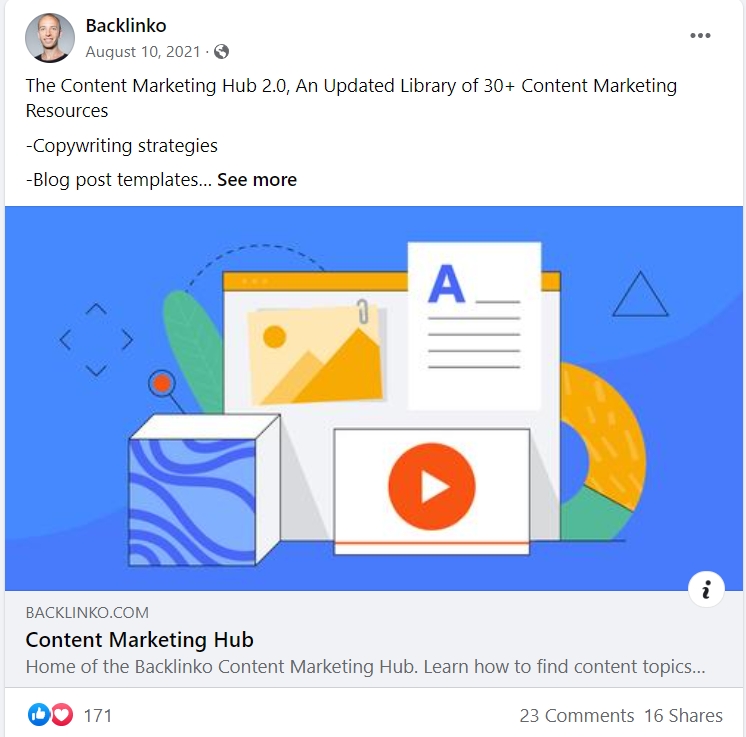
Pages containing errors must be improved and submitted for recrawling..
Click “request indexing” on the inspection result page (which you’ll see right after inspecting the URL).
There is a way of checking the status of a specific page without entering the GSC. Try out our free SEO tools. Just type in several URLs simultaneously and the service will check if the pages are in the index.
In case your sites’ indexing is poor, you might find some useful advice in this article.
What kind of problems did you encounter?
Most frequent indexing issues
1. Pages are not getting indexed at all
If Google user agents ignore your site’s pages, make sure they are allowed to crawl your site.
Check the configuration files and “robots.txt” file — it must not disallow indexing. Chances are that you excluded the page from search results using a server password requirement or HTML elements such as “noindex” tag or “nofollow” link attribute.
Performance graph of a site disallowed to be indexed via “robots.txt”:
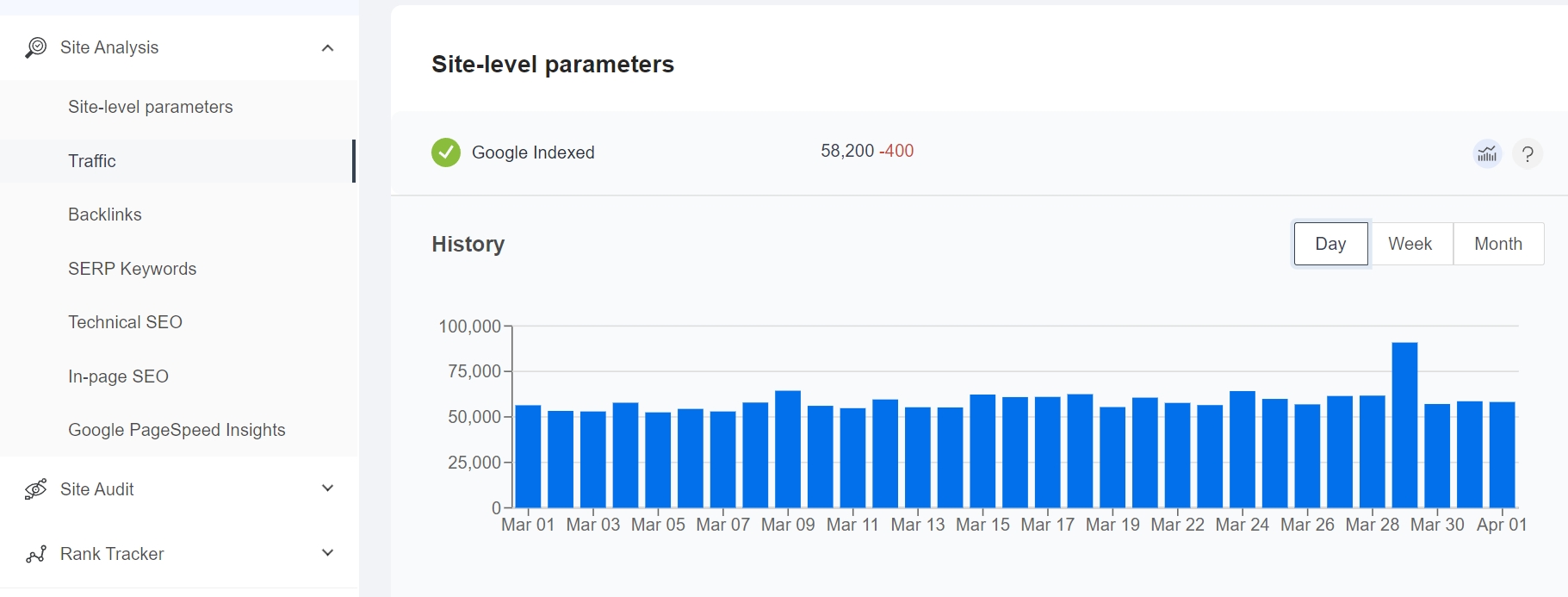
2. Google ignores some of the pages
If your new pages are not getting indexed, chances are that you violated one or several of the search engine’s rules which leads to imposing a penalty. Googlebot also won’t serve your site or some of its pages if it finds them low value or irrelevant to users.
You should figure out which Google Algorithm Filter is imposed, fix the problem and then request Googlebot to recrawl the pages.
3. Indexing takes a long time
There are many reasons why Google bot takes so much time to index new pages. Here are the most frequent ones:
- the contents are rarely updated, thus rarely crawled
- the pages are not optimized well enough
- the pages' internal linking is poor
So, if the pages are not getting crawled, check your access permissions. If some of your pages are not getting indexed, there may be some filters imposed. In no way should you accept a low indexing rate, and here’s what you can do to improve it.
How to improve indexing
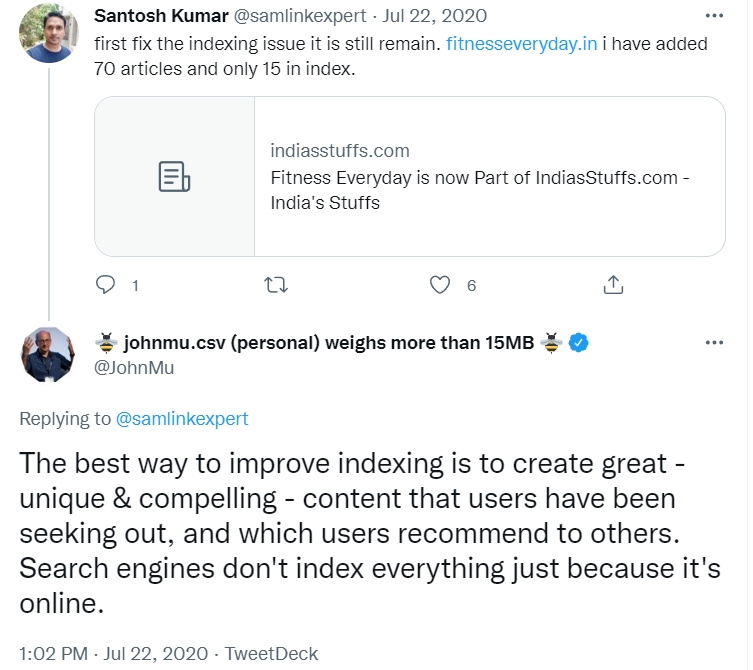
Google representative John Mueller stated the following:
The message is pretty clear isn’t it? But what exactly can you do? Here are some suggestions.
Get your page recrawled
You can manually signal the bot to recrawl particular URLs. Use Google Search Console’s URL Inspection Tool to do so. Open the Console, choose a property, submit the necessary URL and hit the “Request indexing” button.
How to get multiple pages recrawled There is a way to submit for recrawling up to 200 URLs per day We’re talking about a free script by Journey Further, based on the Google Indexing API. To run the script you need a Google Cloud Platform account. Here’s step-by-step instruction
- Install node.js.
- Create a service account on Google Cloud Platform.
- Get your private key JSON file.
- Save it as “service_account.json”.
- Set your service account as an owner (‘delegated’) of the web property you are going to manage.
- Follow this link and enable the indexing API.
- Open the “urls.txt” file and add URLs you want to be crawled.
100 URLs per request batch and 200 URLs per day is the limit for this method. 8. Press Shift+right click to open Windows Power shell. 9. Navigate to the location of the script and enter “node index.js».
If you need more detailed information about the script, check this.
Check the permissions in your “robots.txt” file
“robots.txt” files are used primarily to manage crawler traffic. A webmaster can prohibit bots to visit certain sites, using “disallow”, “nofollow” directives or “noindex”, “none” metatags.
So, next time the bot visits your site, it notices the restrictions and likely obeys them. But you cannot be sure about that. In your robots.txt file you give the bot instructions not commands.
Anyway, you better check that file to see if there’s any restrictions denying the bot access to your site.
###Create a sitemap
A sitemap is needed to help the search bots navigate through your site more efficiently and keep up with updates.
Having a dynamically generated sitemap is a good way to boost indexing speed, since it is automatically updated every time you create a new page, thus it is always up to date. Some website builders, such as Wordpress, WIX or Tilda create a dynamically generated sitemap by default, other CMS use plugins and dedicated services.
You can manually update your sitemap file as well. Google recommends marking recently updated pages in the sitemap using the < lastmod > field. Submit the updated file using the Sitemaps report link. But there’s no need to submit unchanged sitemaps multiple times as Google ignores them. Keep in mind that a sitemap is rather a hint, than a directive. Proper internal linking and site structure are much more important.
Check the structure and internal linking
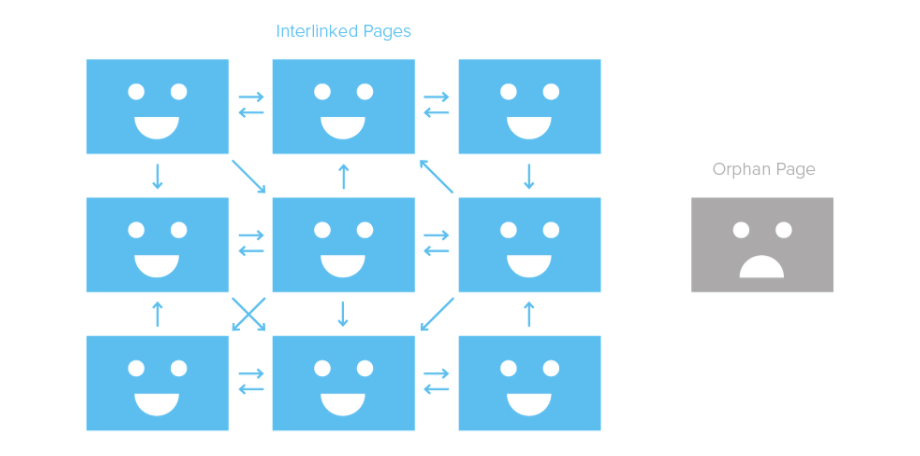
All pages on your site without exception must be internally linked. If a page is not linked to the homepage, or the site’s menu, or other pages on your site, search engines would find it hard to define its relevance. Moreover, they won't be able to scan it, as they couldn’t reach it. Those kinds of pages are called orphan pages. An orphan page missing from the site structure:
 Example from website robbierichards.com/seo/increase-organic-traffic
Example from website robbierichards.com/seo/increase-organic-traffic
You need to attach them to your site structure. As we can see on this diagram, each page is linked to its “parent” category, but they can still be linked to one another.

Example from website web-savvy-marketing.com
You can use this simple example of site structure while creating your own site’s menu.
Now let’s talk about one more important factor which determines a bot's pattern. The number of clicks needed to get to a certain page from the homepage. It’s called Click Distance from Index (DFI). The lower it is, the more important a page will appear, the higher priority it will receive. The bot crawls top priority pages first.
DFI is not always equivalent to the quantity of URL directories. For example, if a bestseller, let’s say, Samsung refrigerator can be accessed from the main page via direct link, its DFI is 2 clicks. But if the product card is located in the catalog or in one of its sections and subsections, directories are numerous, like the following example - site.com/shop/refrigerator/one_chamber_refrigerators/samsung/h_1401_100
If you can’t get a page indexed, check its DFI and location in your site’s structure.
Develop a habit to update your content regularly
Google encourages webmasters to correct, update and expand their content. Googlebot scans regularly updated sites more frequently. Of course, rarely updated sites get crawled less often.
John Mueller of Google recommends adding YouTube videos to your complete and relevant pages. Doing so benefits behavior factors. Plus, adding a new type of content to your site will improve its visibility for the search engine.
Use social networks and other media to get more backlinks
If you are running a corporate account on social media, use it to announce your upcoming materials. You can set up a nice preview for your link via Open Graph Markup. Add a related picture to it, come up with a catchy header and watch your social traffic increase.
Find as many relevant 3rd party platforms as possible and use them to announce and attract attention to your upcoming materials. Links must be natural and related to the site’s contents. Use forums, review aggregators, press-releases, social media, Q&A services and other platforms.
Improve your site’s load time.
Poor response times can seriously harm your site’s indexing rate. According to John Mueller, Googlebot won’t be scanning at its maximum speed, given that average response time is more than one second.
But that’s not the only problem of low loading speed. Almost half of users leave a page if it takes more than 3 seconds to load. Search engines could assume your site to be low-quality and even lower your site’s SERP positions, if it isn’t fast enough.
To boost your site’s speed you have to optimize the code of the above-the-fold section, enable compression with Gzip or Brotli, minify CSS and Java Script and reduce image sizes.
You can check your site’s speed via our service. It analyzes each phase of loading, according to Core Web Vitals parameters.
FAQ: what else affects a site’s indexing speed
How can non-indexed pages determine Google’s attitude to your site?
Google evaluates the quality of your site’s content based on indexed pages only.
Does the “noindex” tag interfere with a page’s indexing after being removed?
According to John Mueller, one won’t have any trouble reindexing a page once tagged “noindex”.
How does redirect affect indexing?
John Mueller claims that the bot, most likely, will not index a live URL, if sent to it via 301 redirect.
How to get your once 404 pages indexed faster?
The indexing of such pages for the first time might take a while. Seroundtable advises to create a new URL for the content and use 301 redirect. Might also try just to request reindexing for that old URL.
How does Google react to hash symbols in URLs?
Google won’t index a URL with hash symbols in it. For example, this URL “https://site.com/news/p/article” is going to be indexed, and this “https://site.com/news/p/article#plan” is not.
Let us know in the comments if we missed anything and what ways of improving indexing you personally know
