Error 404: What It Is and How to Use It for Business
A quick summary of the article
A well-designed 404 page helps you avoid losing customers and organic traffic, doesn't hurt your site's SEO metrics, and can even boost brand trust.
Who should read this article:
- Business and online store owners who want to stop losing leads because of 404 errors.
- SEO specialists and marketers who handle technical SEO and are responsible for organic growth.
- Developers and product teams who work on the site's UX and page logic.
Everyone has seen the "404 Not Found" window. What's behind this code, how a 404 error on a site affects business and SEO, and what to do to keep a user from closing the page — let's break it all down in this article, taking into account the search engine recommendations for 2026.
What is a 404 error and a 404 page on a site?
A 404 error is a page shown to visitors when the requested URL isn't found. "HTTP 404 Not Found" indicates that the server can't find the requested resource. However, the status code only reports that the resource is unavailable — it doesn't specify if this absence is temporary or permanent.
Technically, a 404 is a client-side error: a request was sent, but a page doesn't exist at that address. For the user, it looks like "page not found," and for the site, it's a broken user journey: the person doesn't get the content they were expecting. If these situations happen often and aren't handled, it hurts the user experience and business goals.
For example, site owners often redirect from a 404 error to the homepage instead of providing a clear explanation. This causes confusion and frustration for the user. Customers lose access to the information they expected to find. As a result, potential buyers or readers leave the company.
Besides the 404 error, other 4xx codes are used:
400 Bad Request — An incorrect request from the client due to a syntax error.
401 Unauthorized— Access denied. The request can't be completed because the server requires guest authentication.
403 Forbidden — The request is rejected because the visitor doesn't have permission to access the content for various reasons. Unlike a 401, the site knows the client's identity, but, for instance, registration might be required. Or an administrator has granted access only to specific users. Sometimes this error occurs if the site considers the guest's actions to be spam or hacking attempts and may temporarily block the person to reduce the load on its resources.
410 Gone — The requested resource has been permanently deleted. Unlike a 404 error, which indicates a temporary or accidental unavailability, a 410 explains that the resource is gone for good and won't be back.
FAQ about the 404 error
Are a 404 error and a 404 page the same thing?
The 404 code is the technical status of the server's response, while the 404 page is the specific template you show the user when this code occurs.
What's the difference between a 404 and a 410?
A 404 says, "the page can't be found right now," and a search engine might continue to check the URL for a while. A 410 says, "the page has been permanently deleted," and bots will remove it from their index more quickly.
Should I be afraid of individual 404 pages appearing?
Nope! For Google, properly handled 404s are a normal part of a site's operation. The important thing is to monitor their quantity and causes, not to try and hide every single error.
 Source: amazon.com/error
Source: amazon.com/error
Reasons for 404 Errors on a Website
The reasons for 404 errors on a website are usually as follows:
Server issues. Sometimes, the cause is that the server is temporarily down for technical maintenance or an update. In this case, some requests might return a 404 or a 5xx error, and that's a good reason to check your logs and monitoring systems.
Moving a page without a proper redirect. If developers didn't use a 301 or 302 redirect when moving a URL, users who try to access the old page will see a 404 error.
Deleting a page. This happens when content has been removed — either intentionally or by accident — and there's no redirect to a relevant page or a clear path forward for the visitor.
A typo in the URL address. Often, the reason is simply that a user mistyped the link or clicked on a broken link from an external site.
Auto-generation of non-existent URLs. For example, things like filtering, pagination, UTM tags, or template errors can create URLs for pages that don't actually exist, but bots and users still try to access them.
FAQ on 404 Error Causes
Do I need to fix every single 404 error?
Nope! First and foremost, you should focus on 404s that are getting traffic, have internal links pointing to them, or have external backlinks. The rest can be left as correct server responses.
What should I do if a 404 is happening on a page we deleted?
If there's an obvious replacement, set up a 301 redirect to the current page. If not, you can leave a well-designed 404 or 410 page and suggest alternatives right on that page.
Why are there so many 404s with nonsensical URLs in my reports?
These are often traces left by scanners, bots, or incorrect links. You can generally ignore them if they aren't affecting your users or eating up your server's resources.
How 404 Errors Affect SEO and User Experience
When a search engine encounters a 404 error, it learns that the requested content is no longer available and, over time, removes that URL from its search results. By themselves, proper 404s don't hurt your site's rankings — Google has confirmed this.
What does have a noticeable impact on SEO metrics is losing important pages: those with traffic, good user engagement, and backlinks. In this case, it's crucial to either restore the content or set up a 301 redirect to the most relevant alternative to preserve its authority and traffic.
However, when less significant web pages that don't attract traffic (like old promotional archives or temporary landing pages) run into a 404 error, it has almost no effect on your overall search ranking. Here, a 404 page can actually work as a handy navigator, catching that lost traffic and guiding users to the right sections.
From a user experience perspective, it all comes down to the frequency and quality of how these errors are handled. If a person occasionally sees a well-designed 404 page with a search bar and helpful links, it's not a big deal. But if they constantly hit a "page not found" wall with no way to continue their journey, their trust in the brand drops — and so do conversions.
FAQ: The Impact of 404 Errors on SEO and UX
Do 404 pages hurt a site's rankings in Google?
Nope, not if the errors correctly serve a 404 or 410 HTTP status code and aren't tied to important landing pages. Search engines see this as a normal part of the web.
Should I redirect all 404s to the homepage?
Definitely not. Mass redirects to the homepage create what are known as "soft 404s." Search engines flag these pages as problematic, and users get confused and are more likely to leave.
How do I know which 404s to fix first?
Check your reports in Google Search Console. The important URLs are the ones that have traffic, internal clicks, and external links pointing to them.
 Source: flickr.com/photos/404error1
Source: flickr.com/photos/404error1
Tools for Finding 404 Errors and Broken Links
There are tools out there that make it easier to find weak spots in your site's structure, like broken links, a large number of 404 errors, and soft 404s. The most commonly used are free Google products and specialized SEO tools.
Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a free service from Google that helps you monitor, maintain, and fix issues with your site's presence in Google Search results. With Search Console, you can solve indexing problems and request re-indexing of new or updated content.
You can also get data on your Google Search traffic: find out which queries bring users to your site and how many times they click on your search results. It's also super helpful for seeing which websites are linking to yours.
Search Console is used to optimize your search ranking and keep an eye on your site's overall health. Finding 404 and soft 404 errors is one of the key factors in technical SEO.
How to use it in 2026:
- Log in to Google Search Console and select "Indexing," then "Pages."
- In the "Why pages aren't indexed" section, look for the reasons "Not found (404)" and "Soft 404."
- Click on each reason to see a list of pages, and sort the URLs by impressions and clicks.
- Check each address for typos or incorrect characters, and fix any internal links and navigation.
- If a page is outdated, update its content or set up a 301 redirect to a relevant page. If there's no replacement, just leave a clean 404 or 410 page.
FAQ on Tools for Finding 404s
Is Google Search Console enough to monitor 404 errors?
For basic monitoring, yes. But specialized SEO tools and crawlers can find more technical details and help you gather all your reports in one place.
How often should I check my site for broken links and 404s?
At least once a month for small projects, and every 1-2 weeks for e-commerce sites and large content-heavy websites.
Can I fully trust the reports from webmaster tools?
Sometimes they contain "noise" from bots and experimental URLs. The important errors are the ones that affect real users and your traffic.
 Source: awwwards.com/error1/
Source: awwwards.com/error1/
Why Your Website Needs a Custom 404 Page
Creating a separate 404 page is an absolute must for a healthy website in 2026. It improves the user experience, reduces your bounce rate, and helps you avoid losing leads and sales, even if a user lands on a non-existent URL.
The accompanying text should explain what happened and suggest the next steps: a site search, links to popular sections, your product catalog, blog, or special offers page. This way, the visitor won't just close the tab but will continue exploring your site, and you'll keep them engaged.
If you stick with the standard, generic error page, users will leave your site in a heartbeat — people want to find information right away. They're willing to forgive a glitch, but a template full of confusing technical jargon will just scare them off.
FAQ: Why do I need a custom 404 page?
Can I get by without a custom 404 page?
Technically, yes, but if you do, you're losing traffic and have no control over the user's journey. A custom 404 page is a simple way to guide people back to useful sections of your site.
Is a 404 page important for small businesses and local projects?
Yes! For smaller sites, every single lead and call counts, and a 404 error with no explanation often cuts the customer's journey short.
Do I need to create several different 404 pages for different sections?
It's not a requirement, but for large projects (like marketplaces, banks, or media outlets), it can help you tailor the user's experience more precisely to what they might be looking for.
 Source: ebay.com/n/error
Source: ebay.com/n/error
Guidelines for a Great 404 Page
A Clear Message. It should be obvious that something went wrong or that the page couldn't be found. This helps users understand what happened and avoids confusion.
An Explanation of the Cause. Giving a little extra info about what might have led to the error is helpful for visitors. Standard text variations are often used, like: "The page wasn't found because of a typo in the URL or because the content has been moved."
Useful Links and a Search Bar. Give your visitor a quick way to find the information they need: include links to popular sections, the catalog, the blog, and a site search.
Consistent Style with the Main Site. The 404 page should visually feel like a part of your brand, using your brand colors, illustrations, and tone of voice.
Site Admin Contacts. Adding a link to your contact page or a feedback form allows users to report the error or ask a question, which helps improve the overall user experience.
Navigational Elements. Including links to the main sections of your site or a simplified sitemap helps users find other useful resources on your platform.
A Search Box. This lets the user quickly find the information they need without having to switch tabs or go back to the homepage.
Friendly Design and Style. These make the 404 page feel less intimidating. Creative approaches can grab attention, but this style doesn't work for every brand — sometimes, it's more important to maintain a serious tone.
FAQ: 404 Page Design Guidelines
Is it mandatory to add a search bar to a 404 page?
For e-commerce and large websites, yes, it's critical. For smaller projects, you can get by with just links to popular sections.
Is it okay to use humor on a 404 page?
Yes, if it matches your brand's tone of voice. But remember: the main goal is to help the user find what they need, not just to entertain them.
How many links should be on a 404 page?
The sweet spot is 3–5 links to the most popular sections, plus a search bar. Any more can be overwhelming; any fewer might not provide enough options.
Checklist: How to Set Up Your 404 Page
To make your 404 page work for your business and prevent traffic loss, just follow this handy checklist:
- Check the technical side. Make sure the page returns a 404 or 410 HTTP status code, not a 200. This is crucial for SEO and proper indexing.
- Add clear text. Explain to the user what happened in simple terms. Try to avoid technical jargon without explaining it.
- Include a site search bar. This is especially important for e-commerce sites and content-heavy projects — it's the quickest way to guide the user back to the information they need.
- Provide links to popular sections. Your product catalog, blog, special offers, contact info—give users options to continue their journey on your site.
- Maintain a consistent style. The 404 page should look like a part of your website, not a separate element. Use your brand's colors, fonts, and illustrations.
- Set up monitoring. Regularly check your reports in Google Search Console to keep an eye on important 404s that have traffic and backlinks.
- Fix critical errors. For pages with traffic, set up 301 redirects to relevant alternatives. Don't just redirect all 404s to the homepage — this creates soft 404s.
- Test and improve. Analyze user behavior on your 404 page using Google Analytics, and test different versions of your text and design.
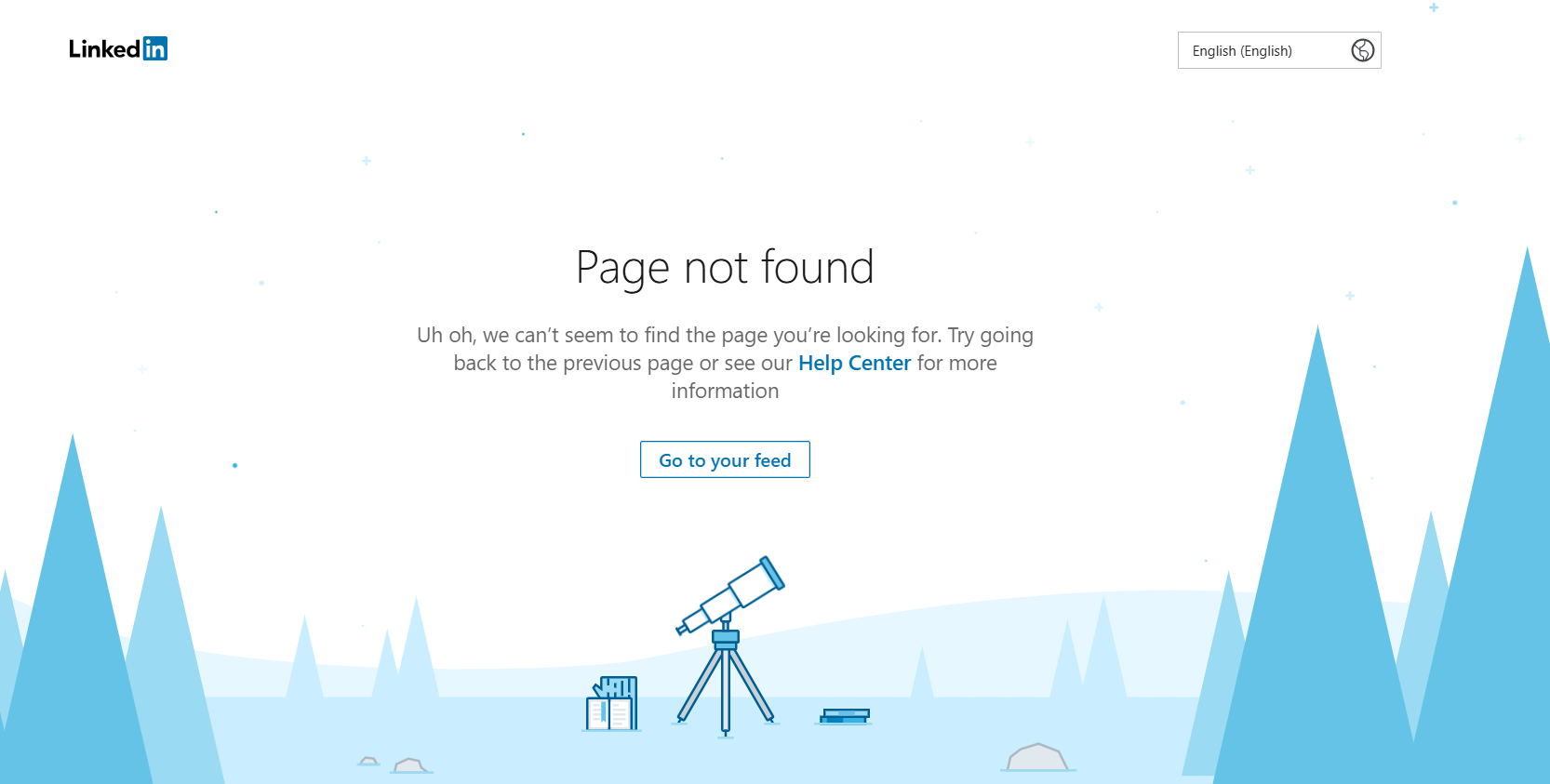 Source: linkedin.com/error
Source: linkedin.com/error
The 404 Error as a Business Tool
A 404 error and a "Page Not Found" page aren't problems to be hidden, but rather an opportunity to win back lost traffic and build brand trust. Today, search engines confirm that correctly configured 404s don't hurt your SEO, as long as they are set up properly and aren't linked to important landing pages.
Here are the main principles for handling 404 errors:
- Serve the correct HTTP code (404 or 410) for non-existent pages, and avoid mass redirects to the homepage.
- Create a user-friendly 404 page with a search bar, helpful links, and a style that's consistent with your main site.
- Monitor important 404s with traffic and backlinks, and set up 301 redirects to relevant alternatives.
- Regularly check your site for broken links using Google Search Console and specialized SEO tools.
Remember: every 404 error is a potentially lost customer. But a well-designed 404 page turns that loss into a chance to keep the user engaged and guide them to the right parts of your site.
🍪 By using this website, you agree to the processing of cookies and collection of technical data to improve website performance in accordance with our privacy policy.